Critical Minerals and Energy Intelligence
Graphite
Graphite demand is expected to surge over the next decade, fueled by the rapid adoption of electric vehicles, expansion of energy storage systems, and growth in advanced industrial applications.
Demand for graphite almost quadruples by 2040, according to the IEA’s net-zero emissions scenario.
Investors should prepare for volatility in the graphite market, as prices respond to supply chain risks, China’s dominance in mining and processing, evolving export controls, and the race to build new capacity outside China.
Graphite Insights
Latest News
What is graphite
Graphite is a naturally occurring form of crystalline carbon (atomic number 6), renowned for its unique combination of high thermal stability, electrical conductivity, and lubricating properties1. It appears as a soft, gray to black mineral and is one of only two naturally occurring forms of pure carbon, the other being diamond. Graphite’s structure consists of layers of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, allowing the layers to slide over each other easily—this underpins its use as a lubricant and in pencils.
The name “graphite” derives from the Greek word graphein, meaning “to write,” reflecting its long-standing use in writing materials.
Today, graphite is indispensable for a wide range of industrial and technological applications, including steelmaking, batteries, refractories, lubricants, and emerging clean technologies.
Why graphite matters: strategic applications
Batteries and energy storage
graphite is the dominant anode material in lithium-ion batteries, accounting for up to 95% of the anode composition. The rapid growth of electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage is driving unprecedented demand for both natural and synthetic graphite
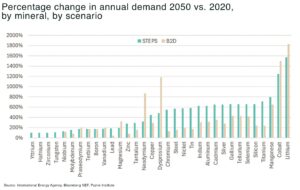
the battery sector is projected to be the fastest-growing application for graphite, with demand expected to rise by more than 1,400% between 2020 and 2050
Steelmaking
in the steel industry, graphite is used as a carbon raiser to adjust carbon content in molten steel and as a lubricant in high-temperature processes
the steel sector remains one of the largest consumers of graphite globally
Refractories and foundries
graphite’s high thermal resistance makes it essential in refractories for lining furnaces, crucibles, and molds in metal production
expanded graphite and graphite foils are used in high-performance gaskets and fire-resistant materials
Lubricants and industrial uses
thanks to its layered structure, graphite is an effective dry lubricant for machinery operating under extreme temperatures or conditions
it is also used in brake linings, foundry facings, and as a component in advanced composites
Emerging technologies
graphite is increasingly used in fuel cells, lightweight composites, and as a precursor for graphene, a material with revolutionary potential in electronics and materials science
Supply and Demand Dynamics
Production concentration
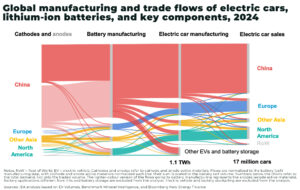
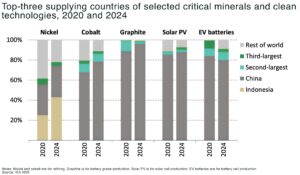
China dominates global graphite supply, followed by India and Brazil34. This concentration creates significant supply chain vulnerabilities, especially as geopolitical tensions and export controls intensify
the US and EU have classified graphite as a critical raw material and are seeking to diversify sources, including new projects in Kazakhstan and North America
Natural vs. Synthetic Graphite
natural graphite is mined, while synthetic graphite is produced from petroleum coke. Synthetic graphite is less exposed to Chinese supply risks but is more energy-intensive to produce
both types are essential for battery applications, but natural graphite is currently facing a supply deficit, while synthetic graphite has experienced a temporary oversupply
Market trends
the global graphite market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 9.41% from US$15.90 billion in 2025 to US$24.93 billion by 2030, driven by surging demand in batteries and energy storage
by 2050, graphite supply will need to increase nearly 500% to meet clean energy and electrification targets, requiring the development of hundreds of new mines worldwide
Mining and processing
graphite is mined using both open-pit and underground methods, then beneficiated through crushing, grinding, flotation, and sometimes acid leaching to achieve high purity
after concentration, graphite is classified by flake size and carbon content to suit various industrial needs
environmental management is increasingly important, with efforts to minimize air and soil contamination during processing
Graphite’s unique properties and critical role in the global energy transition make it a linchpin for both established industries and emerging technologies. As battery demand surges and supply chain security becomes paramount, graphite’s strategic importance is set to grow sharply in the coming decades.

US launches $12 billion strategic minerals stockpile
The US will establish a US$12 billion strategic minerals stockpile, marking its most direct intervention yet in critical mineral markets as competition with China intensifies.
The next energy shock won’t be oil — it’ll be critical minerals, warns IEA
Key takeaways The International Energy Agency’s World Energy Outlook 2025 redefines energy security for the electric age: not oil or gas, but critical minerals are

US to build $1 billion critical mineral stockpile as supply risk deepens
The US Department of Defense is preparing to purchase $1 billion worth of critical minerals to build a national stockpile and shield military supply chains

Why the US fails to secure critical mineral supply — and how it can be fixed
An inside look into what’s gone wrong in Washington — and how to fix it In December 2024, China banned exports of gallium, germanium, and antimony
Critical minerals demand to surge up to 135% on defense and 400% on power generation and storage
Key Takeaways The estimated demand growth for ten key critical minerals for defense through 2035 is between 80%-250%, rising on average 135% over the next

Gold, uranium, tungsten, graphite, other metals, exempted from US global tariffs with new Trump directive
US president Donald Trump has issued a new executive order exempting gold bullion, uranium, tungsten, graphite, and several other metals from global tariffs, effective Monday,