Critical Minerals and Energy Intelligence
Nickel
The transformation of Indonesia into a global nickel producing powerhouse by Chinese investment has transformed the nickel market, bringing record amount of nickel onto the market.
But, demand is projected to double by 2030, driven by the energy transition and electric vehicles. And, as the West looks to secure an independent supply of “clean” nickel with big government investments, new opportunities are opening up — just as concerns grow that ore grades in Indonesia are falling.
Nickel Insights
Industry nickel report
The supply of nickel Class I, essential for electric batteries, is expected to face a shortage for the next 3-5 years, according to our new report. The Oregon Group predicts a continued crunch in the nickel market despite increased production by Chinese nickel giant, Tsingshan.
Report: The Green Economy and Nickel's Generational Class I Supply Crunch
Latest infographics on nickel:
Nickel (Ni)
Nickel, atomic number 28, is a lustrous, silvery-white metal celebrated for its strength, ductility, and outstanding resistance to corrosion and heat. With a melting point of 1,455°C, nickel is a cornerstone of modern industry, playing a pivotal role in stainless steel production, battery technology, and advanced alloys.
As the global economy pivots toward electrification and sustainability, nickel’s importance continues to rise-especially in electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, and next-generation manufacturing.
Why nickel matters: strategic applications
Electrification and clean energy
Nickel is indispensable in the clean energy transition due to its unique properties:
-
electric vehicles (EVs): nickel is a critical component in lithium-ion battery cathodes, particularly in high-nickel chemistries that boost energy density and extend driving range. The growth of EVs is a primary driver of new nickel demand
-
renewable energy infrastructure: nickel alloys are used in wind turbines, solar panels, and grid-scale batteries, supporting the expansion of green energy worldwide
-
hydrogen economy: researchers are exploring nickel’s role in hydrogen fuel cells and electrolyzers, further cementing its place in the low-carbon future
Stainless steel and advanced alloys
-
stainless steel: roughly 70% of global nickel consumption goes into stainless steel, where it imparts corrosion resistance, strength, and durability for use in construction, transportation, and consumer goods
-
aerospace and high-performance applications: nickel-based superalloys are essential for jet engines, gas turbines, and other demanding environments due to their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive conditions
Industrial, medical, and specialty uses
-
medical devices: nickel’s biocompatibility makes it suitable for surgical instruments, implants, and dental applications
-
industrial equipment: nickel alloys are used in food processing, chemical plants, and marine engineering for their resistance to acids, alkalis, and saltwater
Supply and demand dynamics
Demand drivers
-
EV and battery growth: the rapid adoption of electric vehicles and grid storage is fueling robust demand for high-purity nickel
-
urbanization and infrastructure: stainless steel demand remains strong as emerging markets invest in construction and transportation
-
technological innovation: new uses for nickel in hydrogen, renewables, and advanced manufacturing are expanding the market
Supply challenges
-
market surplus: the global nickel market is forecast to be in a significant surplus in 2025, with production expected to reach 3.735 million metric tons, outpacing usage by nearly 200,000 metric tons
-
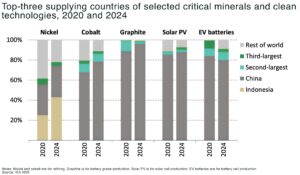
price volatility: nickel prices have hit five-year lows in early 2025 amid oversupply, regulatory uncertainty, and shifting trade policies. Indonesia, the world’s largest producer, has introduced royalty hikes and faces delays in mining permits, creating ore tightness despite high refined output
-
resource concentration: Indonesia accounts for over half of global nickel production, making the market vulnerable to policy shifts and supply disruptions. The Philippines is considering export bans that could further impact global supply chains
Major producers
-
Vale S.A. (Brazil/Canada): one of the world’s largest nickel miners, with operations in the Americas and Asia
-
BHP Group (Australia): a leading producer focused on sustainable mining and supplying the battery sector
-
Anglo American (Brazil/Australia/South Africa): a major player investing in low-carbon nickel sulfate for EV batteries
Market trends shaping nickel’s future
-
clean energy transition: despite the current surplus, long-term demand for battery-grade nickel is expected to surge as EV adoption and renewable energy accelerate
-
sustainability and recycling: the industry is investing in recycling technologies and sustainable mining to reduce environmental impacts and secure supply
-
geopolitical dynamics: trade policies, resource nationalism, and regulatory changes in top producing countries are reshaping the nickel market and supply chains
Nickel’s unique combination of strength, conductivity, and corrosion resistance makes it essential for electrification, stainless steel, and advanced manufacturing. As the world transitions toward cleaner energy and smarter technologies, nickel’s strategic value will remain robust-cementing its role as a foundation of the modern industrial economy.

Indonesia orders world’s biggest nickel mine to cut ore quota for 2026
PT Weda Bay Nickel has been told to file a 2026 work plan reflecting 12 million wet metric tonnes of annual production and sales, a

Can nickel prices hit $25,000 in 2026?
Indonesia’s new nickel supply strategy Indonesia — the world’s dominant producer with two-thirds of nickel supply — has signaled major supply cuts for 2026, triggering
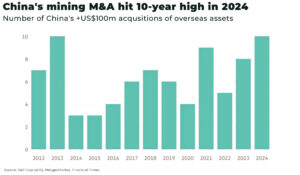
The next energy shock won’t be oil — it’ll be critical minerals, warns IEA
Key takeaways The International Energy Agency’s World Energy Outlook 2025 redefines energy security for the electric age: not oil or gas, but critical minerals are

Why the US fails to secure critical mineral supply — and how it can be fixed
An inside look into what’s gone wrong in Washington — and how to fix it In December 2024, China banned exports of gallium, germanium, and antimony

Is this the “shale moment” for critical mineral mining in the US?
A quiet revolution is underway in the bedrock of the global economy. The mining and processing of critical minerals — from lithium to rare earths,
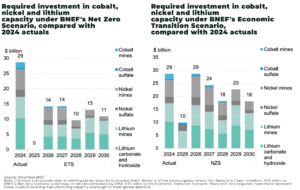
Battery metals demand set to quadruple by 2040
Global demand for battery metals is forecast to x4 over the next 15 years, even as near-term growth moderates, according to BloombergNEF’s latest Electric Vehicle